STMicroelectronics Wireless Charging Solutions for Wearable Devices
Foreign Object Detection (FOD) is an important step in the design of wireless charging products. This feature detects the presence of foreign objects between the transmitting and receiving coils and cuts off the power supply immediately. When a metal object is placed in the magnetic field of the transmitting coil, eddy currents are induced on the metal, causing the metal temperature to rise rapidly.
Innovation will be the key to product success. Wireless charging is one of the emerging technologies that is developing rapidly. Electromagnetic induction charging is the most mainstream wireless charging technology, followed by resonant wireless charging. The Wireless Power Consortium is responsible for maintaining and developing various wireless charging application standards, including the Qi standard for wireless charging of smartphones and portable devices with power up to 15W.
In addition to charging batteries, wireless charging technology can also directly power devices. In many industrial applications, wireless power can enhance the freedom of movement of robotic arms. In medical and beauty devices, wireless power can achieve product sealing design, which is convenient for disinfection before subsequent use.
STMicroelectronics provides wireless charging chips with power ranging from 1W to 100W. The STWLC38 is a Qi 1.3 certified wireless power receiver chip optimized for space-constrained product applications such as wearable devices and headsets, with a maximum power of up to 15W and a total area (including peripherals) of only 7mm x 7mm. The STWLC38 can be used in conjunction with the STWBC86 transmitter chip.
The STWLC38 uses a 2.1mm x 3.3mm WLCSP40 package (wafer-level chip size package) and an adjustable output voltage from 4V to 12V with a resolution of 25mV. The processor core is an ARM 32-bit Cortex™-M0+ with a maximum main frequency of 64MHz, and the memory includes 64KB ROM, 16kB RAM, and 32kB RRAM that can store firmware patches like flash memory.
Foreign object detection (FOD) is an important part of the wireless charging product design process. This function can detect the presence of foreign objects between the transmitting coil and the receiving coil and cut off the power supply in time. When a metal object is placed in the magnetic field of the transmitting coil, eddy currents are induced on the metal, causing the metal temperature to rise rapidly. The STWLC38 can accurately measure voltage and current, and has built-in multiple protection measures to monitor overcurrent, overvoltage and overheating.
The STWBC86 is a power transmitter compatible with the Qi1.2.4 wireless charging standard, with a maximum transmission power of 5W under the Qi standard protocol. It is a single-chip solution with an integrated full-bridge inverter, and is also equipped with an ARM 32-bit Cortex™-M0+ core with a main frequency of 64MHz and 8 kB RAM, as well as 8 kB FTP (multi-time programmable memory) for installing firmware patches. The design is optimized for the Qi standard A11a topology and uses a low-on resistance inverter to improve energy efficiency.
Changing charging from wired to wireless is a big challenge for developers. To simplify the development process, ST has launched two mature solutions. The STDES-WLC38WA (Figure 1) and STDES-WBC86TX (Figure 2) form a complete solution for wireless charging for wearable applications, and are equipped with PCB Gerber files, firmware, software, design guidelines, and technical specifications to facilitate users to develop PCB circuit boards and use them as plug-and-play devices. The PCB area is 7mm*7mm (Figure 3), which is particularly suitable for space-constrained devices.
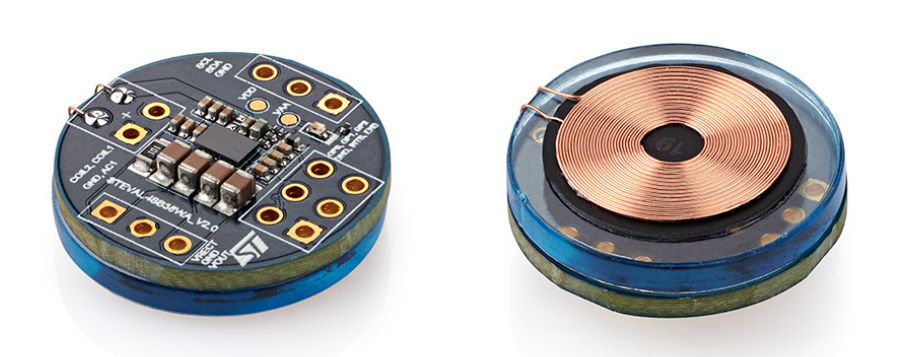
Figure 1: STDES-WLC38WA wearable device wireless charging receiver board based on STWLC38
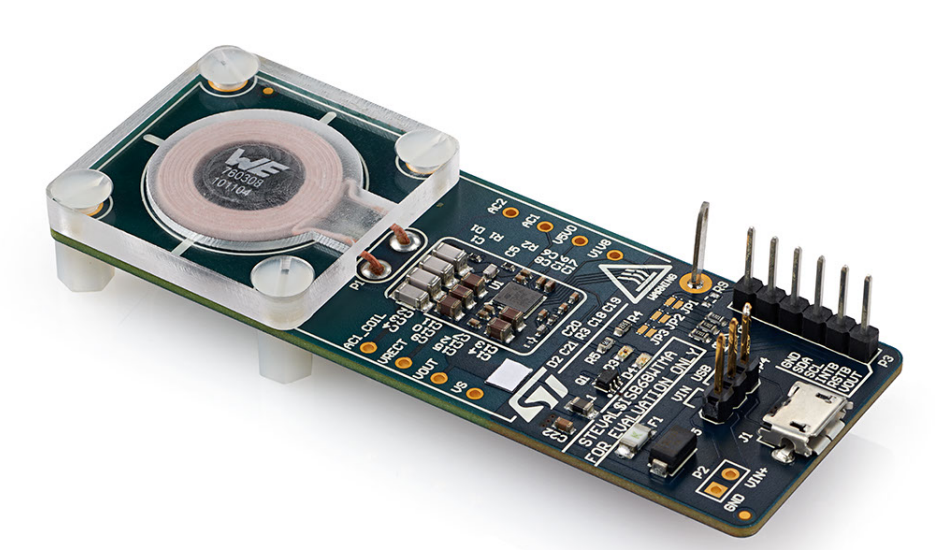
Figure 2: STDES-WBC86TX wireless charging transmitter board based on STWBC86
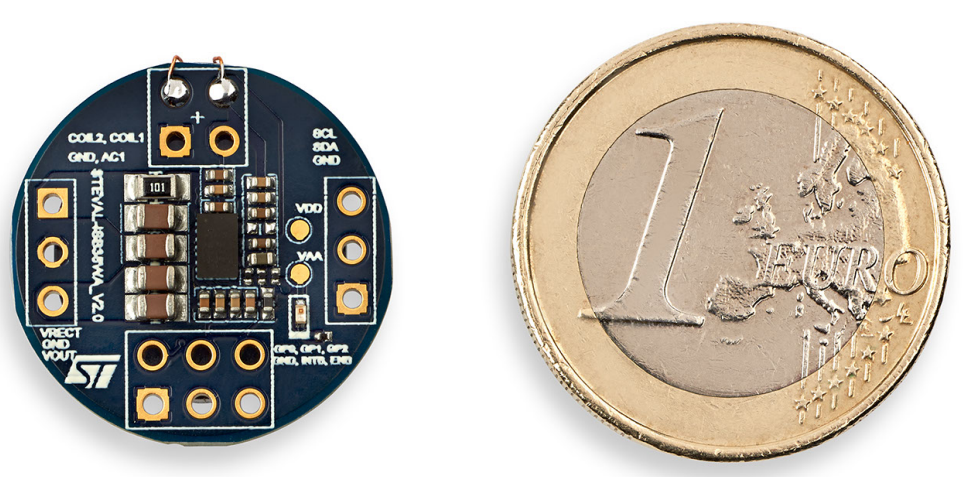
Figure 3: STDES-WLC38A compared with a one-dollar euro coin
STDES-WLC38TWS (Figure 4) is an existing mature TWS (True Wireless Stereo) charging box solution. The custom coil (Figure 5) is optimized for the TWS shell, allowing users to easily build wireless charging solutions. With these reference designs, developers can significantly shorten their time to market.
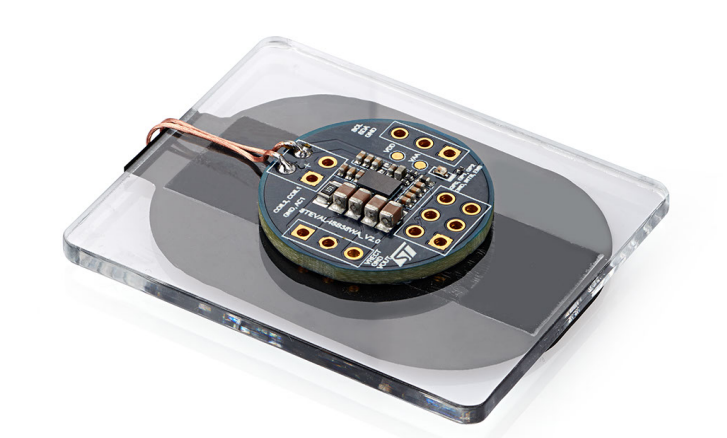
Figure 4: STDES-WLC38TWS wireless charging receiver board based on STWLC38RX
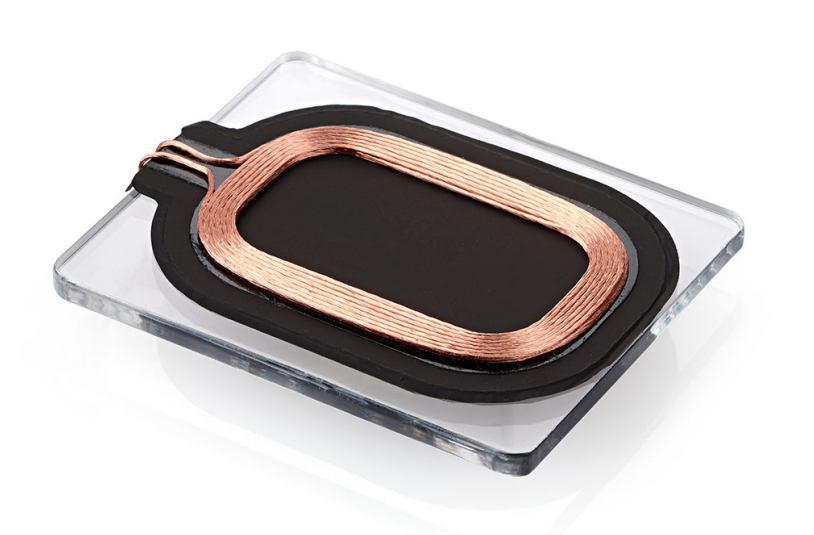

Figure 5: Custom coil for STDES-WLC38TWS wireless charging receiver board
The STWLC38 has the best energy efficiency in its class in the 5W to 15W power range (Figure 6).
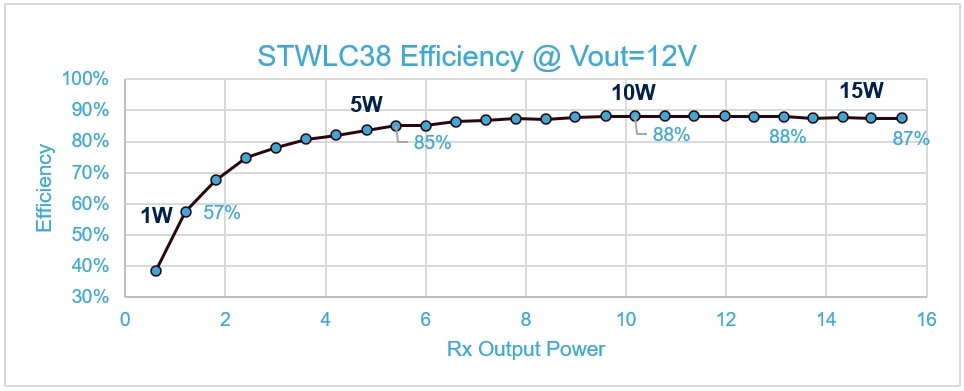
Figure 6: Energy efficiency vs. receiver output power
The user experience of wireless charging depends largely on whether the charger is convenient and easy to use. Of course, misalignment between the transmitter and the receiver will affect the wireless charging effect. The last thing we want to see is a phone or earphones on the charger for two hours without charging at all!
ST has introduced a patented technology called "ARC, or Adaptive Rectifier Configuration", which allows the device to charge normally even if the receiver and transmitter are misaligned by up to 50%. This greatly improves the user experience. Users can charge their smartwatches by simply placing them on the charger without worrying too much about aligning the watch with the charging coil.
ST's receiver IC also enables another excellent application scenario - reverse charging. Users can turn a wireless receiver into a wireless transmitter or charger. For example, users can use a smartphone with an ST receiver chip to charge a device such as a smartwatch or another smartphone.
